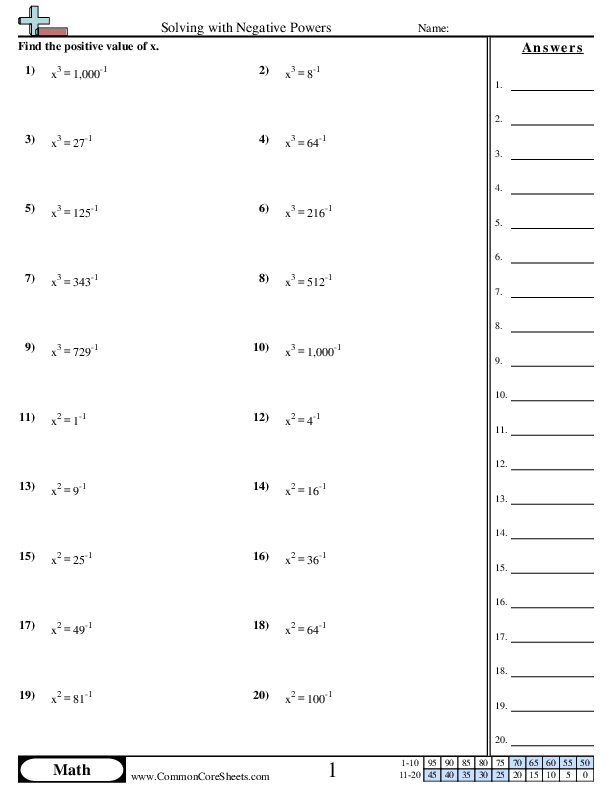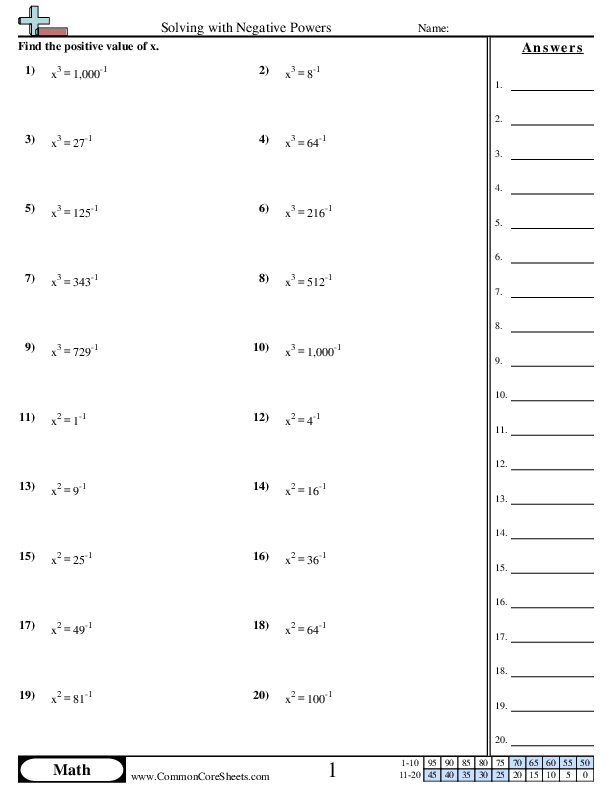Previous Standard
Know that numbers that are not rational are called irrational. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; for rational numbers show that the decimal expansion repeats eventually, and convert a decimal expansion which repeats eventually into a rational number.
Next Standard
Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. For example, 32 × 3–5 = 3–3 = 1/33 = 1/27.
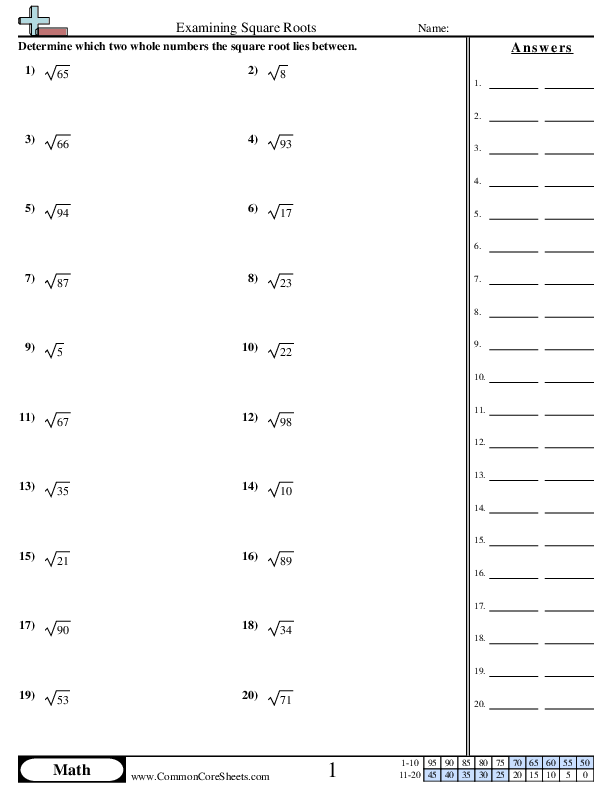
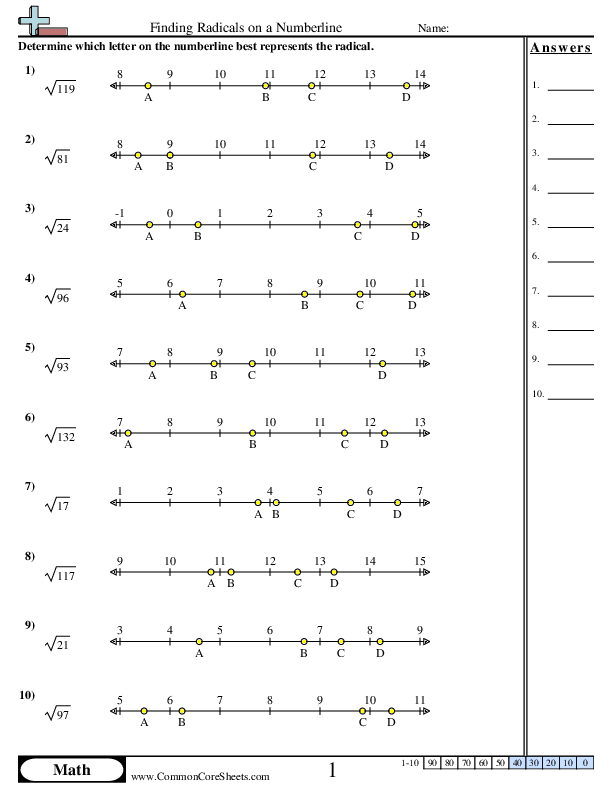
For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of √2, show that √2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations.
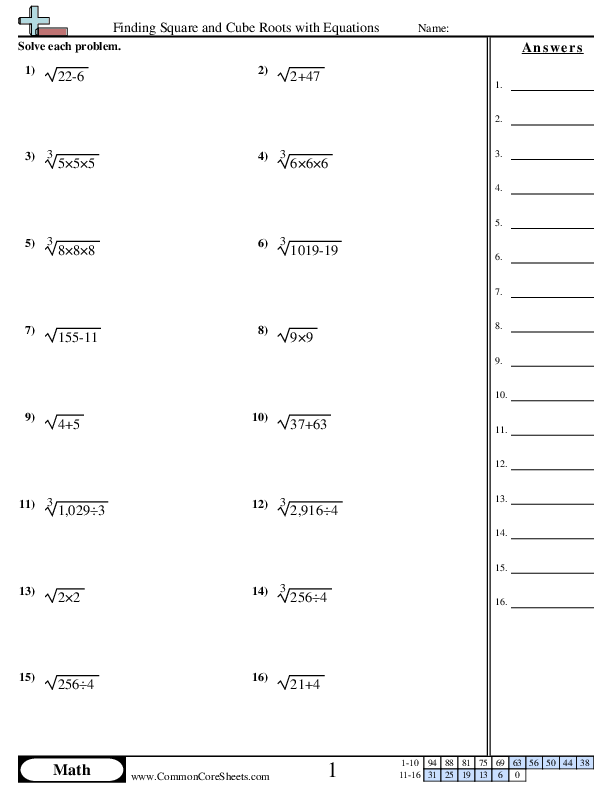
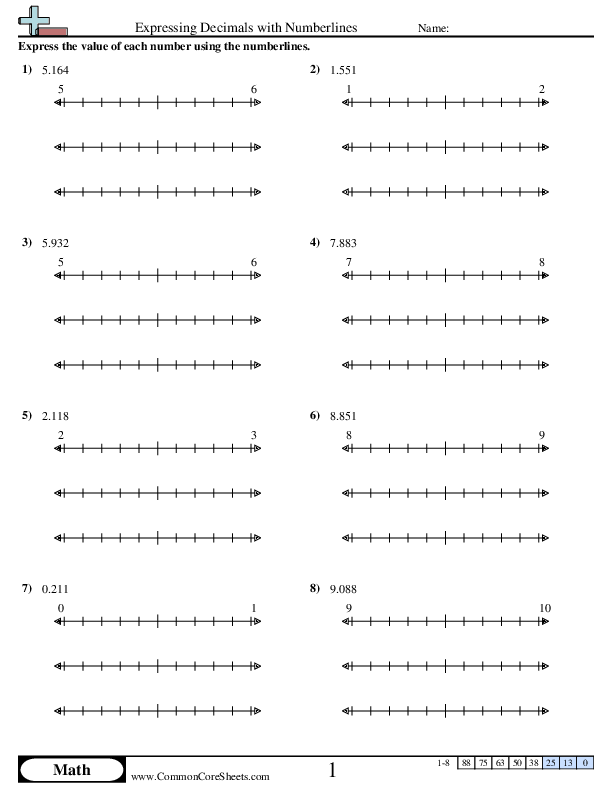
Worksheets